Week 33 of pregnancy marks an important stage in the third trimester, as your baby experiences rapid growth and final developmental changes before birth. At this point, your baby measures about 43–45 cm in length and weighs approximately 1.9–2.1 kg.
Your baby is now practicing sucking, swallowing, and breathing movements—skills essential for feeding after birth. The liver continues storing iron, while the brain forms millions of new neural connections each day. Both mother and baby undergo significant changes, making this week crucial for monitoring health and recognizing warning signs.
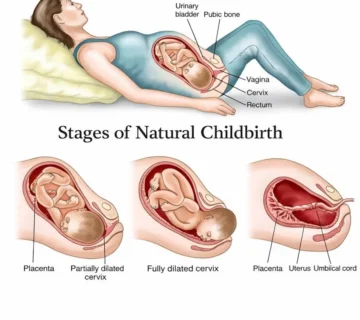
Fetal Development in week 33 pregnancy
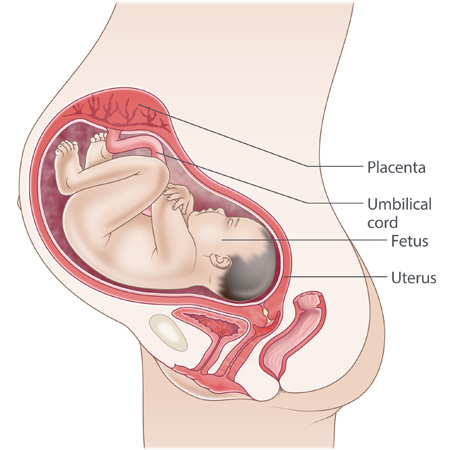
Overall Growth and Development
By week 33, your baby’s organs, skeleton, and major systems are fully formed but still maturing. With limited space inside the uterus, fetal movements become more deliberate but often slower and stronger. The amniotic fluid also reaches its peak volume around this time.
Key developments include:
-
Rapid brain growth and increased neural connections
-
Fully developed fingernails and growing hair
-
Stronger bones, though the skull remains flexible
-
Continuous practice of breathing movements
-
Iron storage in the liver for early infancy
Fetal Movements in week 33 pregnancy
Despite the reduced space, fetal movements should remain regular and noticeable. You may feel:
-
Strong kicks
-
Stretching movements
-
Rolling or shifting
-
Hiccups
What Counts as Normal?
A healthy baby should move at least 10 times in under 2 hours during kick counts.
When to Be Concerned?
Seek medical attention if:
-
Movements decrease significantly
-
You feel fewer than 10 movements in 2 hours
-
Movements stop for 12 hours
Decreased movement may signal reduced oxygen supply or concerns related to the placenta or umbilical cord.
Fetal Position in week 33 pregnancy
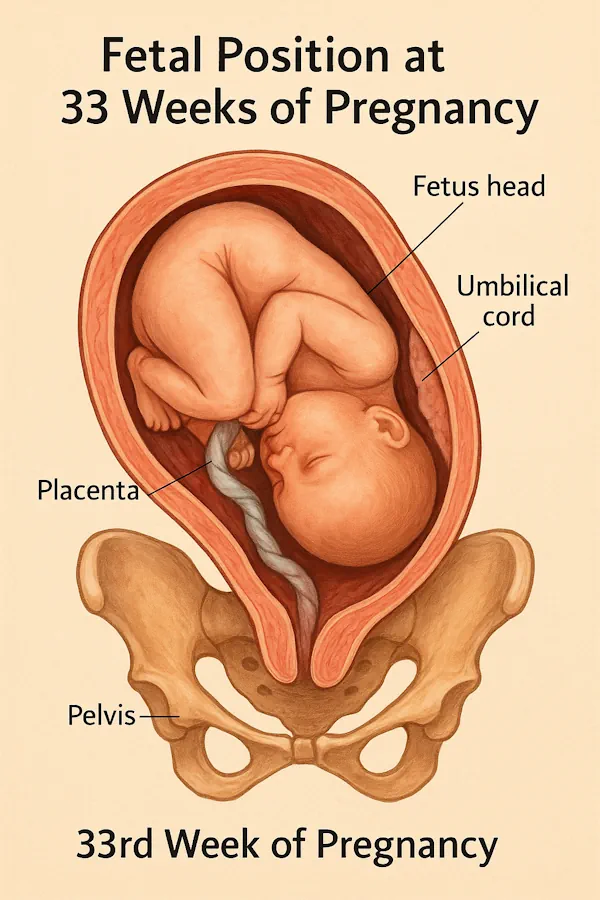
Around this time, many babies begin to settle into their final birth position.
1. Cephalic Position (Head-Down)
The ideal position for a vaginal birth. Most babies achieve this by weeks 32–36.
2. Breech Position
Includes frank breech, complete breech, and footling breech.
Many breech babies still turn by week 36.
3. Transverse Lie
Baby lies sideways across the uterus.
Usually resolves naturally by week 34–36.
When Position Becomes a Concern
Persistent breech or transverse position after week 36 may require:
-
External Cephalic Version (ECV)
-
Planned Cesarean section
Mother’s Symptoms and Body Changes in week 33 pregnancy
Physical Changes
-
Shortness of breath
-
Pelvic pressure
-
Frequent urination
-
Back pain
-
Difficulty finding a comfortable sleeping position
-
Heaviness in the abdomen
Common Pains
-
Lower back pain
-
Pelvic and groin discomfort
-
Leg cramps
-
Round ligament pain
These usually improve with rest and proper posture.
Braxton Hicks Contractions
Practice contractions that are:
-
Irregular
-
Mild
-
Relieved by rest
They differ from true labor contractions, which become regular, stronger, and do not stop with rest.
Shortness of Breath
Due to the uterus pressing against the diaphragm.
Seek medical help if shortness of breath is:
-
Sudden
-
Severe
-
Accompanied by chest pain or rapid heartbeat
Vaginal Discharge
Normal:
-
White or clear
-
Mild odor
Abnormal (seek medical help):
-
Green, yellow, or foul-smelling discharge
-
Itching or burning
-
Continuous watery discharge (possible membrane rupture)
Heartburn and Appetite Changes
Caused by pressure on the stomach.
Helpful tips:
-
Eat small, frequent meals
-
Avoid spicy and fatty foods
-
Do not lie down after eating
Insomnia and Fatigue
Due to discomfort, fetal movements, and anxiety.
Best sleeping position:
On the left side with a pillow between the knees.
Swelling of Hands and Feet
Mild swelling is normal.
Sudden swelling of the face or hands + headache = Warning for preeclampsia
Emotional Changes
-
Anxiety about labor
-
Mood swings
-
Increased sensitivity
Totally normal due to hormonal changes.
Nutrition and Exercise in week 33 pregnancy
Nutrition for Baby’s Brain Development (DHA)

During the third trimester, your baby’s brain grows rapidly—up to three to four times its earlier size. DHA (an omega-3 fatty acid) is essential for:
-
Brain development
-
Neural communication
-
Vision maturation
Best sources of DHA:
-
Salmon, trout, sardines
-
DHA-enriched eggs
-
Walnuts
-
Fish oil supplements (with doctor’s approval)
Food Safety During Pregnancy

To prevent foodborne illness, avoid:
-
Raw or undercooked eggs
-
Raw sushi
-
Unpasteurized dairy
-
Undercooked meat
-
Deli meats unless reheated
-
Leftovers older than 24 hours
Always:
Wash hands, sanitize surfaces, cook meat thoroughly, refrigerate foods promptly.
Safe Exercises in week 33 pregnancy
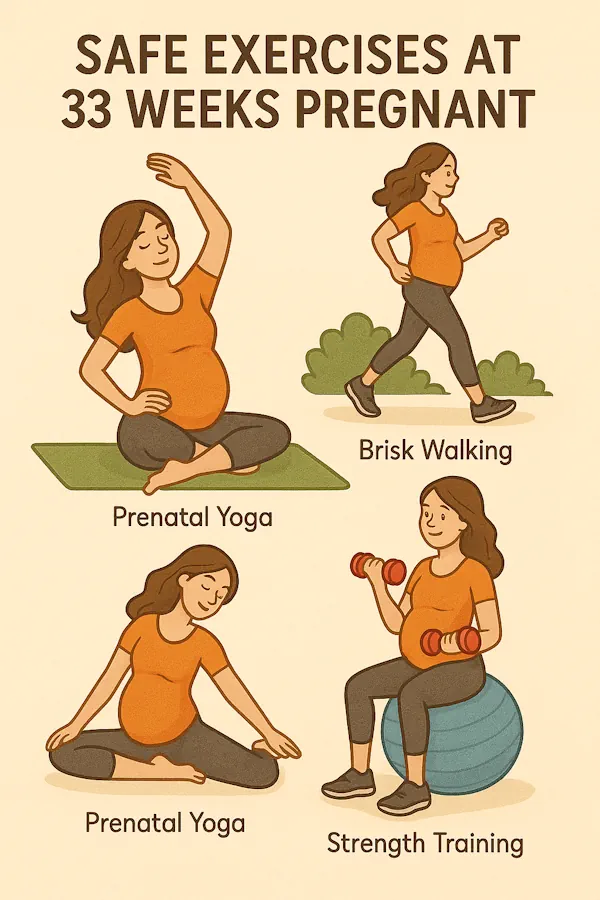
-
Swimming
-
Prenatal yoga
-
Gentle stretching
-
Pelvic floor exercises (Kegel)
Avoid:
-
Heavy lifting
-
Contact sports
-
High-impact workouts
Medical Care in week 33 pregnancy
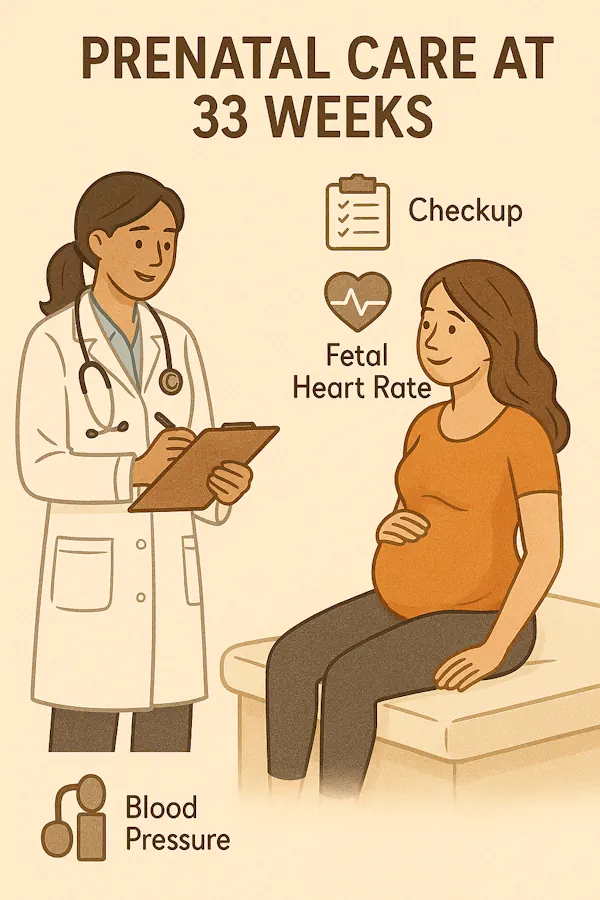
Routine Checkups Include:
-
Blood pressure measurement
-
Fundal height measurement
-
Weight monitoring
-
Listening to fetal heart rate
-
Checking for swelling
Ultrasound May Assess:
-
Fetal weight
-
Position
-
Amniotic fluid volume
-
Placenta function
-
Umbilical artery blood flow (if necessary)
Warning Signs You Should Not Ignore
-
Vaginal bleeding
-
Severe abdominal pain
-
Persistent headache
-
Blurred vision
-
Sudden swelling
-
Loss of fluid
-
Reduced fetal movements
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is an episiotomy necessary?
Usually not.
Episiotomy is now used only when medically required, such as:
-
Fetal distress
-
Assisted delivery (forceps, vacuum)
-
Shoulder dystocia
Perineal massage from week 34 may reduce the need for episiotomy.
2. Should I record my labor and delivery?
You may, but:
-
Movement of the camera operator may disturb medical staff
-
Your partner may miss the emotional experience
If you choose to film, record only key moments and coordinate with your care team.
3. Can I breastfeed with flat or inverted nipples?
Yes. Most mothers can breastfeed successfully.
Tools that may help:
-
Nipple shields
-
Manual suction before feeding
-
Consultation with a lactation specialist
4. What month is week 33 pregnancy?
You are in the 8th month of pregnancy.
5. Is birth at week 33 pregnancy dangerous?
It is considered preterm.
Babies usually require NICU care but have excellent survival rates with proper medical support.
6. Can I fly during week 33?
Most airlines require a doctor’s note after week 32.
Travel is not recommended unless necessary.
7. Is swelling normal?
Mild swelling is normal.
Sudden swelling of the face or hands is concerning for preeclampsia.
Final Summary
Week 33 of pregnancy is a dynamic and important stage for both mother and baby. Your baby continues refining essential survival skills while gaining weight and strengthening the brain and nervous system. Meanwhile, your body undergoes significant physical and emotional changes as it prepares for labor.
Focus on:
-
A healthy, nutrient-rich diet
-
Safe physical activity
-
Monitoring fetal movements
-
Attending regular prenatal appointments
-
Recognizing the warning signs that require immediate care
With proper awareness and medical follow-up, you can confidently and safely navigate this crucial phase of pregnancy






No comment