Entering week 28 of pregnancy marks the beginning of the third trimester—a stage where your baby grows faster than ever and your body experiences new physical and hormonal shifts. At this point, your baby can open and close their eyes, respond to sounds, and follow a more structured sleep–wake cycle. Their brain is developing rapidly, and the nervous system has matured enough to start helping with basic temperature regulation.
For the mother, symptoms such as shortness of breath, heartburn, back pain, leg swelling, and increased fatigue are common. This week also includes important prenatal tests like the glucose tolerance test, Rh screening, and anemia evaluation to ensure the health of both mother and baby.
This guide provides evidence-based, easy-to-understand information about fetal development, maternal changes, essential tests, amniotic fluid concerns, warning signs, and self-care tips for week 28 of pregnancy.
Fetal Development in Week 28 of Pregnancy
Fetal Size and Weight
By week 28, your baby typically measures:
-
Length: 36–38 cm (14–15 inches)
-
Weight: around 1–1.1 kg (2.2–2.4 lbs)
The skin is still slightly wrinkled but will continue to smooth out as more fat accumulates under the skin.
Opening and Closing of the Eyes
A major milestone this week is the ability to open and close the eyelids. Many babies also have fully formed eyelashes. They can detect changes in light and may react to bright illumination outside the womb.
Brain and Nervous System Growth
The brain is undergoing rapid development:
-
Billions of neurons continue forming
-
Neural connections (synapses) are increasing
-
By birth, the brain will make up about 12% of the baby’s body weight
-
The central nervous system now helps with basic temperature regulation
Your baby’s brain after birth will continue to grow quickly, which is why newborns need fat-rich nutrition, including breast milk.
Thumb-Sucking and Movements
Reflexes strengthen around this time, and babies may:
-
Suck their thumb
-
Bring their hands near their face
-
React to familiar voices
These behaviors help prepare for feeding after birth.
Placenta and Amniotic Fluid
-
The placenta keeps growing and now weighs around 420 grams
-
Blood flow increases to support rapid fetal growth
-
Amniotic fluid continues to protect the baby, help lung development, and provide space for movement
Maternal Symptoms and Body Changes at 28 Weeks

1. Shortness of Breath
As the uterus expands upward, it places pressure on the diaphragm. Increased blood volume also affects breathing. Mild shortness of breath is normal.
Seek medical attention if it is accompanied by chest pain or dizziness.
2. Back and Pelvic Pain
Hormone-driven ligament loosening and weight gain may cause:
-
Lower back pain
-
Pelvic discomfort
-
Hip and thigh aches
Supportive pillows, proper posture, stretching, and maternity belts can help.
3. Heartburn and Indigestion
Hormones relax the esophagus, causing acid reflux. Eating smaller meals and avoiding heavy foods helps reduce symptoms.
4. Braxton Hicks Contractions
These are mild, irregular practice contractions.
⚠️ Seek help if contractions become regular, painful, or closer than every 10 minutes.
5. Increased Vaginal Discharge
Thin, white, odorless discharge is normal.
Abnormal discharge (yellow, green, foul-smelling, or itchy) may indicate infection.
6. Swelling of Feet and Ankles
Mild swelling is common.
Sudden or severe swelling may indicate preeclampsia—especially with headaches or vision changes.
7. Fatigue
The body works harder in the third trimester. Iron deficiency may worsen fatigue.
8. Round Ligament Pain
Sharp or pulling pains in the lower abdomen are common due to uterine stretching.
Amniotic Fluid Assessment in the Third Trimester

Polyhydramnios (Excess Amniotic Fluid)
A rare condition where fluid levels are higher than expected.
Possible Causes:
-
Gastrointestinal obstruction in the baby
-
Uncontrolled gestational diabetes
-
Large-for-gestational-age fetus
-
Twin pregnancy
-
Sometimes no identifiable cause
Risks (if severe):
-
Preterm labor
-
Abnormal fetal positioning
-
Maternal breathing difficulty
Most cases are mild and manageable with monitoring.
Oligohydramnios (Low Amniotic Fluid)
Occurs in about 3–5% of pregnancies.
Possible Causes:
-
Placental insufficiency
-
Small rupture of the membranes
-
Fetal growth restriction (FGR)
-
Maternal dehydration
Risks:
-
Limited fetal movement
-
Umbilical cord compression
-
Poor lung development (if severe)
Management:
-
Increased hydration
-
Frequent ultrasounds
-
Doppler studies
-
Hospital monitoring in severe cases
Key Tests and Checkups in Week 28
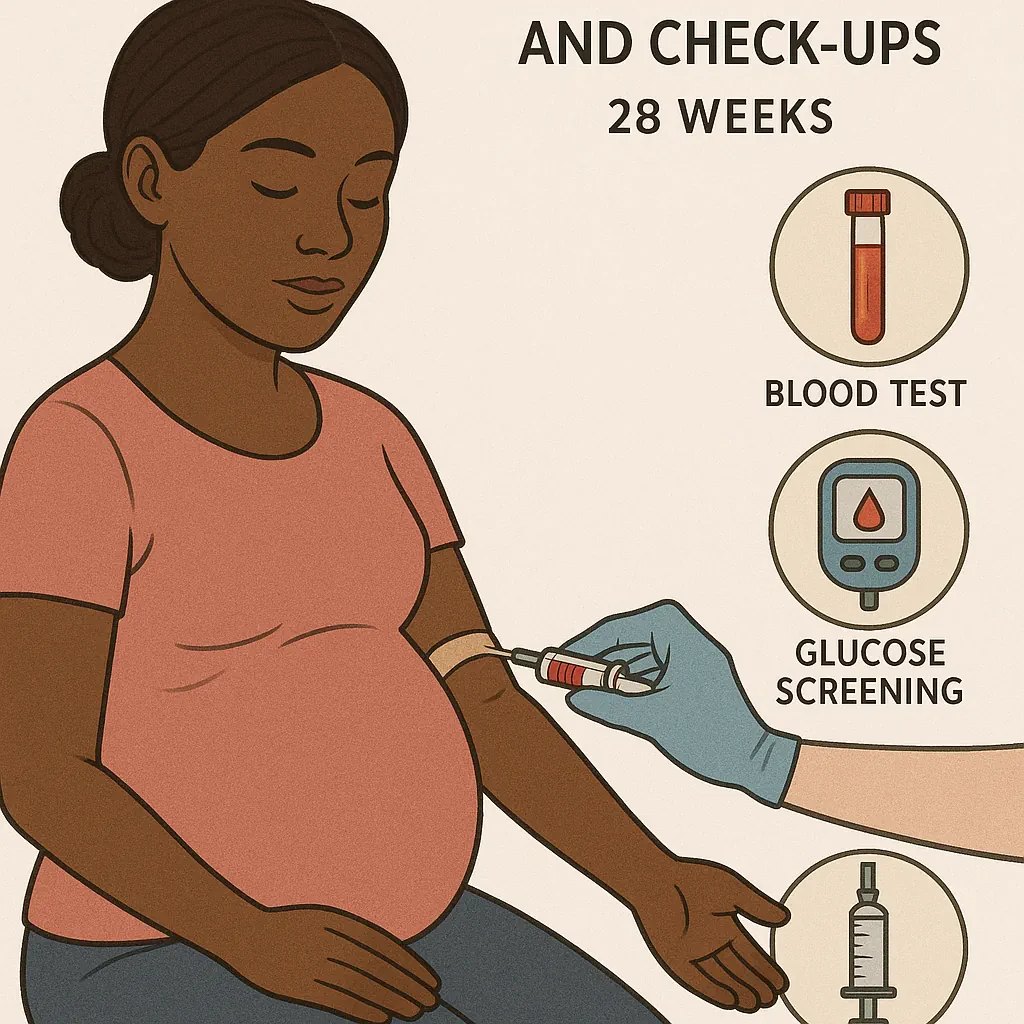
1. Glucose Tolerance Test (GCT)
Screening for gestational diabetes.
-
Drink a glucose solution
-
Blood test 1 hour later
-
No fasting required
If results are abnormal → a longer GTT test is performed.
2. Hematocrit (HCT) Test for Anemia
Checks for iron-deficiency anemia.
3. Rh Factor Screening & RhoGAM Shot
If the mother is Rh-negative, a RhoGAM injection is given between weeks 26–28 to prevent antibody formation.
4. Syphilis Screening (if not done earlier)
Prevents transmission to the baby.
5. Routine Checkup Includes:
-
Blood pressure
-
Weight
-
Fundal height
-
Fetal movement assessment
-
Swelling evaluation
-
Urine check (if needed)
When to Contact Your Doctor Immediately at 28 Weeks
Seek urgent medical care if you experience:
-
Decreased fetal movements (less than 10 movements in 2 hours)
-
Vaginal bleeding
-
Leaking or gush of fluid (possible membrane rupture)
-
Regular, painful contractions
-
Severe headache, vision changes, or upper abdominal pain
-
Sudden or severe swelling of hands, face, or feet
-
Fever above 38°C (100.4°F)
-
Severe abdominal or pelvic pain
These may indicate preeclampsia, infection, preterm labor, or fetal distress.
Nutrition & Lifestyle Tips for Week 28

1. Include Dairy—Especially Yogurt
Provides calcium, protein, and probiotics.
2. Avoid Low-Carb Diets
Healthy carbs such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes support energy and fetal growth.
3. Stay Hydrated
8–10 glasses of water daily support amniotic fluid balance and prevent constipation.
4. Eat Small, Frequent Meals
Helps reduce heartburn and maintain stable energy levels.
5. Maintain Healthy Weight Gain
About 0.4–0.5 kg per week in the third trimester.
6. Safe Physical Activity
Walking, prenatal yoga, stretching, and breathing exercises are ideal.
7. Prioritize Sleep
Sleeping on the left side improves blood flow.
8. Support Emotional Well-being
Prenatal classes, relaxation techniques, and communication with your partner help reduce stress.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Should I store my baby’s cord blood?
It is optional. Families with genetic or blood disorder history may benefit more.
2. Are childbirth preparation classes helpful?
Yes—week 28 is an ideal time to begin.
3. Can the mode of delivery be predicted at week 28?
Sometimes, if conditions like placenta previa, breech position, or large fetal size exist. Final decisions are usually made around week 36–38.
4. How many fetal movements should I feel?
At least 10 movements within 2 hours.
5. Is sex safe at 28 weeks?
Yes—unless your doctor has advised against it due to risk factors.
Conclusion
Week 28 marks a crucial transition into the third trimester. Your baby’s development accelerates, your body undergoes new changes, and essential tests help ensure a safe pregnancy. With proper nutrition, rest, hydration, and awareness of warning signs, you can confidently navigate this stage and prepare for the weeks leading up to birth.

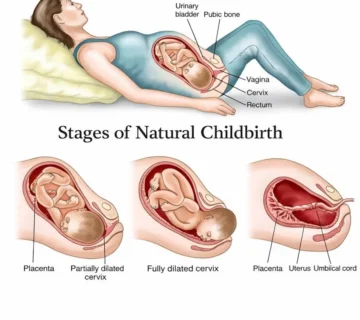




No comment