The fortieth week of pregnancy is one of the most stressful weeks for many mothers. This is the time when anticipation for labor reaches its peak, yet labor pain may still not have begun. At this stage, your baby measures approximately 52 centimeters in length and has reached a weight close to birth — roughly the size of a small pumpkin.
Despite the limited space in the uterus, fetal movements in the fortieth week of pregnancy should not stop or significantly decrease. A noticeable reduction in fetal movements at this stage can be an important warning sign and requires immediate evaluation by a specialist in obstetrics and gynecology.
In this article, we comprehensively review how many months the fortieth week of pregnancy represents, the condition of the fetus at 40 weeks, what to do if labor pain has not started, and when further evaluation or labor induction may be necessary.
What Happens Inside the Fetus in the Fortieth Week of Pregnancy
By the fortieth week of pregnancy, the fetus is almost fully ready for birth. At this stage, the baby typically appears plump, with approximately 15% of body weight consisting of fat, which plays a crucial role in regulating body temperature after birth.
The average fetal weight at 40 weeks is approximately 3 to 3.5 kilograms, and the length is about 52 centimeters.
Most of the fine body hair (lanugo) has disappeared by this time; however, the baby’s skin remains covered with a natural protective layer. This white, greasy substance, known as vernix caseosa, protects the skin from amniotic fluid exposure and from contact with air after birth.
During this week, the fetus produces bilirubin, a substance generated from the breakdown of red blood cells. During pregnancy, bilirubin is transferred through the placenta to the mother’s body for elimination. After birth and clamping of the umbilical cord, the newborn must eliminate bilirubin independently. This process may take several days, and if bilirubin levels rise, the baby may develop neonatal jaundice.
Neonatal jaundice is typically characterized by yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. In most cases, it is not a cause for concern and can be effectively treated with phototherapy.
At 40 weeks of pregnancy, the fetus has a well-developed ability to hear sounds and can recognize the mother’s voice better than any other. From both a neurological and physical standpoint, the baby is fully prepared to meet you.
Babies Weighing More Than Four Kilograms in the Fortieth Week of Pregnancy

Infants weighing more than 4 kilograms are classified as macrosomic infants and may be at increased risk for certain health complications affecting both the mother and the baby. Delivery of a large baby may be associated with a higher risk of prolonged labor, labor arrest, shoulder dystocia, and neonatal hypoglycemia.
Mothers who experience excessive weight gain during pregnancy or who have gestational diabetes are at greater risk of delivering a macrosomic infant. Nevertheless, many of these babies are born completely healthy, and in many cases, vaginal delivery is possible without complications.
If an obstetrician suspects fetal macrosomia, ultrasound examination may be requested. Ultrasound estimates fetal weight by measuring the head circumference and diameter, which represent the largest part of the fetus. However, it is important to note that ultrasound provides only an estimate, and the only definitive way to determine fetal size is at birth.
If neither the mother nor the fetus has a medical complication and the cervix is not yet ready for labor, physicians usually avoid unnecessary intervention. Many women of smaller stature are able to deliver large babies vaginally without difficulty, whereas some women with larger body frames may experience challenges even with smaller infants.
Your Body in the Fortieth Week of Pregnancy
If labor has not yet begun during the fortieth week of pregnancy, it is completely normal to feel fatigued, restless, and frustrated. Many women repeatedly ask themselves:
“Is there anything I can do to make labor start sooner?”
While your physician may prefer waiting a few more days, it is important to understand that most home remedies for inducing labor either lack proven effectiveness or work only under specific conditions.
Home Remedies for Starting Labor: Fact or Myth?
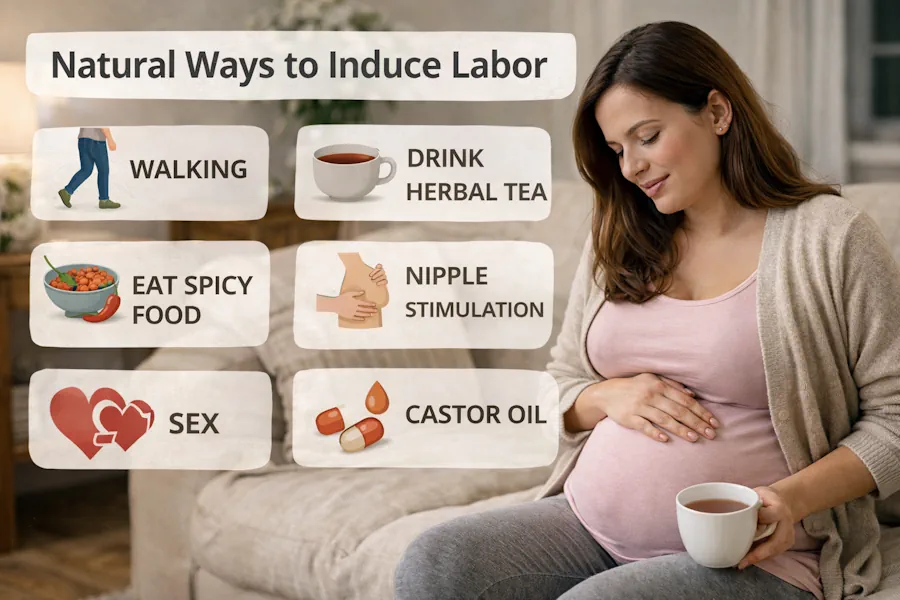
Many commonly suggested methods among pregnant women are not scientifically supported. Although most are not dangerous, some may be uncomfortable or even harmful.
For example, consuming spicy foods, chocolate, or caffeine with the belief that they trigger labor usually results only in indigestion, acid reflux, and ankle swelling, without playing a meaningful role in initiating labor.
Walking in the Fortieth Week of Pregnancy: Effective or Not?
Many people believe that walking can initiate labor. Theoretically, gravity may help the baby descend and apply pressure on the cervix.
However, in reality:
-
Walking alone does not initiate labor
-
It may only be effective if the cervix is already partially dilated
-
In most cases, contractions stop once walking is discontinued
Nevertheless, light and regular walking, if medically permitted, is beneficial for circulation, mood, and overall physical readiness.
Castor Oil for Labor Induction: Why It Is Not Recommended
Some women use castor oil to stimulate labor. However:
-
Castor oil is a strong laxative
-
Its most common effects are severe diarrhea, dehydration, and weakness
-
It has no reliable effect on initiating labor
For these reasons, this method is generally not recommended.
Herbal Remedies and Acupuncture
Although herbal teas and medicinal herbs are popular for inducing labor:
-
There is insufficient scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness
-
Some studies suggest they may even increase the likelihood of prolonged pregnancy
Research findings on acupuncture are inconsistent, and it cannot be considered a reliable method for inducing labor.
Nipple Stimulation: The Only Supported Home Method
The only home method with some scientific support is nipple stimulation.
This practice triggers the release of oxytocin, a hormone that:
-
Causes uterine contractions
-
Functions similarly to the medication Pitocin
⚠️ Important considerations:
-
Must be performed three times daily, each session lasting about one hour
-
May cause strong and sudden contractions
-
Can affect the fetal heart rate
For this reason, physicians usually recommend nipple stimulation only under hospital supervision.
Ultimately, Patience Is the Best Option
In general, labor is a natural process, and whenever possible, it is best to allow the body and baby to determine the appropriate timing. Even if labor is delayed by several days, this is usually not a cause for concern.
Abdominal Muscle Separation (Diastasis Recti) in Late Pregnancy

Many pregnant women, especially in late pregnancy, may notice a gap along the midline of the abdomen known as diastasis recti. This condition:
-
Occurs in approximately one-third of pregnancies
-
Is usually not painful
-
Results from separation of the two parallel abdominal muscles
Main causes include:
-
Pressure from the enlarged uterus
-
Genetic predisposition
-
Softening of connective tissue
-
Weak abdominal muscles
How to Strengthen Abdominal Muscles in the Fortieth Week
Strengthening abdominal muscles can help:
-
Reduce back pain
-
Improve postpartum recovery
-
Prevent post-pregnancy complications
Safe exercises in late pregnancy
Abdominal breathing
Take a deep breath, and during exhalation, gently contract your abdominal muscles.
Pelvic tilt
Lean against a wall or assume a hands-and-knees position, then tighten abdominal muscles during exhalation.
If Labor Is Delayed in the Fortieth Week
In many cases, delayed labor results from miscalculation of gestational age.
Important facts:
-
Up to 9 days of delay is normal
-
80% of babies are born between weeks 38 and 42
-
Only 1 in 10 babies is born after 42 weeks
What Happens If Pregnancy Reaches Week 41?

If pregnancy extends beyond 41 weeks:
-
Fetal movements are monitored more closely
-
Non-stress testing (NST) is performed
-
Ultrasound evaluates amniotic fluid volume
These tests are painless and assess fetal well-being.
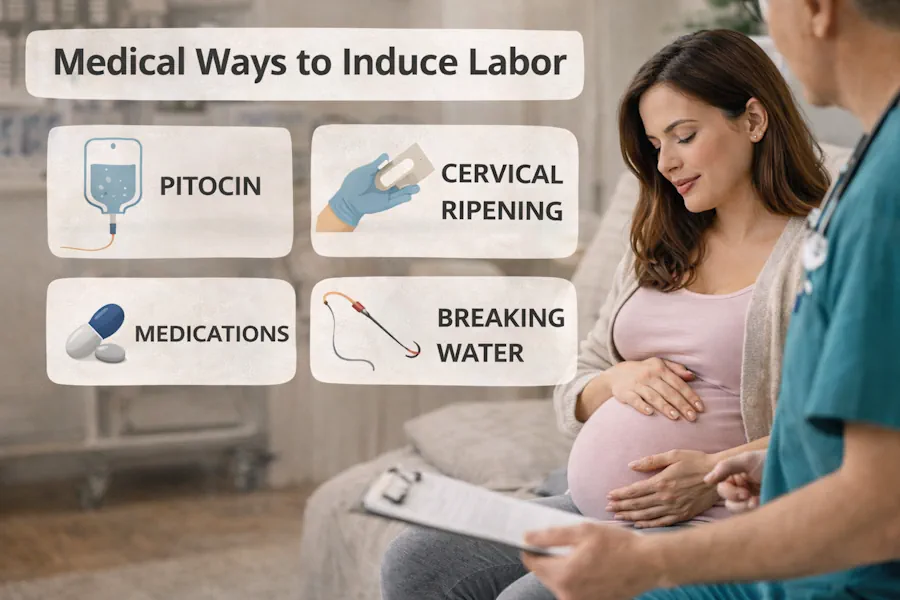
Labor Induction: When and How?
Labor induction may be recommended when:
-
Pregnancy reaches 41 or 42 weeks
-
The placenta loses efficiency
-
Amniotic fluid decreases
-
Fetal movements diminish
Medical Methods for Initiating Labor
Membrane Stripping
Cervical stimulation to release prostaglandins
⚠️ Performed only if the cervix is dilated
Cervical Ripening
Mechanical or pharmacological methods to prepare the cervix
Amniotomy
Artificial rupture of membranes
If labor does not begin within 24 hours, Pitocin is typically administered
Pitocin Administration
A synthetic form of oxytocin that:
-
Produces stronger and more regular contractions
-
Requires continuous monitoring in a hospital setting
Risks After 42 Weeks of Pregnancy
After 42 weeks, risks increase, including:
-
Neonatal respiratory problems
-
Postmaturity syndrome
-
Poor tolerance of labor stress
-
Increased likelihood of cesarean delivery
In these cases, labor induction or cesarean section may be lifesaving.
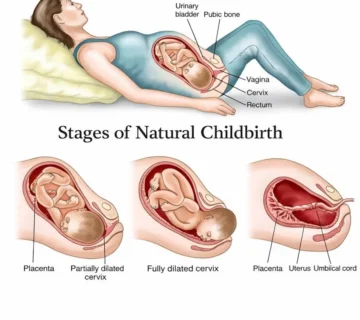
Signs of Labor in the Fortieth Week of Pregnancy

As the body prepares for labor, some signs may appear days before labor, while others indicate active labor.
Signs of approaching labor
Lightening (baby dropping)
-
Less pressure on the abdomen
-
Easier breathing
-
Increased pelvic and bladder pressure
Increased vaginal discharge
-
Cervical preparation
-
Gradual loss of the mucus plug
Irregular contractions (false labor)
-
Irregular
-
Improve with rest
-
Do not cause cervical dilation
Signs of true labor
Regular, painful contractions
-
Become stronger and more frequent
-
Do not stop with rest
-
Typically occur every 5–10 minutes
Rupture of membranes
-
Sudden gush or slow leakage of fluid
-
Requires immediate hospital evaluation
Lower back and abdominal pain
-
Begins in the lower back
-
Radiates to the abdomen and pelvis
-
Intensifies with each contraction
Diarrhea or mild nausea
-
Caused by hormonal changes
Difference Between True and False Labor
| True Labor | False Labor |
|---|---|
| Regular and progressive | Irregular |
| Does not stop with rest | Improves with rest |
| Increasing intensity | Variable intensity |
| Causes cervical dilation | No cervical change |
When Should You Go to the Hospital?
Seek immediate medical care if you experience:
-
Regular contractions every 5 minutes for at least 1 hour
-
Rupture of membranes
-
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
-
Significant decrease in fetal movements
Nutrition in the Fortieth Week of Pregnancy

Proper nutrition plays a key role in maintaining maternal energy, preparing for labor, and supporting fetal health.
Dietary principles
-
Light yet nutrient-dense meals
-
Small, frequent portions
-
Prevention of bloating and reflux
Recommended foods
-
Whole grains (whole wheat bread, brown rice, oats)
-
Lean proteins (poultry, low-mercury fish, eggs, legumes)
-
Fruits and vegetables
-
Healthy fats (olive oil, avocado, nuts)
-
Adequate fluids
No specific diet has been proven to initiate labor. Foods such as pineapple or dates are popular beliefs but lack strong scientific evidence.
Exercise in the Fortieth Week of Pregnancy

Safe, gentle exercise can:
-
Reduce fatigue
-
Improve circulation
-
Ease back pain
-
Support physical and emotional readiness
Recommended activities
-
Light walking
-
Gentle stretching
-
Breathing exercises
-
Pelvic tilts
-
Cat–cow movement
Avoid
-
High-impact or strenuous exercise
-
Running
-
Complex balance movements
-
Prolonged supine positions
Exercise does not directly start labor but may help prepare the body.
Frequently Asked Questions – Fortieth Week of Pregnancy
Is it normal to be 40 weeks pregnant and still have no labor pain?
Yes. It is completely normal to reach the fortieth week of pregnancy without experiencing labor pain. Many healthy pregnancies continue until 41 or even 42 weeks. The absence of contractions at 40 weeks does not necessarily indicate a problem, as long as fetal movements are normal and medical evaluations are reassuring.
What should I do if I am 40 weeks pregnant and labor has not started?
If labor has not started at 40 weeks:
-
Monitor fetal movements daily
-
Stay active with light walking, if approved by your doctor
-
Maintain proper hydration and nutrition
-
Attend all scheduled prenatal appointments
Do not attempt labor induction methods without medical advice. If fetal movement decreases or unusual symptoms appear, seek medical evaluation promptly.
How many months pregnant am I at 40 weeks?
Forty weeks of pregnancy corresponds to the end of the ninth month and is considered full-term pregnancy.
What is the normal fetal weight at 40 weeks of pregnancy?
The average fetal weight at 40 weeks is approximately 3 to 3.5 kilograms (6.6–7.7 pounds). Babies weighing more than 4 kilograms (8.8 pounds) are considered macrosomic.
Is it dangerous for pregnancy to continue beyond 40 weeks?
Pregnancy beyond 40 weeks is not automatically dangerous. However, after 41 weeks, the risk of complications such as:
-
Decreased amniotic fluid
-
Reduced placental function
-
Decreased fetal movements
may increase. For this reason, closer monitoring or labor induction is often recommended after 41 weeks.
What are the risks after 42 weeks of pregnancy?
After 42 weeks, the risks increase significantly and may include:
-
Postmaturity syndrome
-
Respiratory complications in the newborn
-
Poor tolerance of labor stress
-
Higher likelihood of cesarean delivery
In these cases, induction of labor or cesarean section is usually advised to protect maternal and fetal health.
Can walking really start labor at 40 weeks?
Walking alone does not reliably initiate labor. It may help with:
-
Improving circulation
-
Encouraging fetal descent
-
Supporting overall comfort
Walking is most helpful when the cervix is already partially dilated, but it should not be relied upon as a guaranteed method to start labor.
Can diet or specific foods trigger labor at 40 weeks?
There is no scientifically proven food that can reliably start labor. Foods such as dates, pineapple, or spicy meals are commonly mentioned, but strong medical evidence supporting their effectiveness is lacking. Moderate consumption is generally safe unless contraindicated by your physician.
Is nipple stimulation safe for inducing labor?
Nipple stimulation can promote the release of oxytocin, which may trigger uterine contractions. However:
-
Contractions can become strong and sudden
-
Fetal heart rate changes may occur
For these reasons, nipple stimulation should be attempted only under medical supervision, preferably in a hospital setting.
What are the early signs that labor is approaching?
Signs that labor may be approaching include:
-
Baby “dropping” into the pelvis (lightening)
-
Increased vaginal discharge or loss of the mucus plug
-
Irregular contractions (Braxton Hicks)
-
Mild back pain or pelvic pressure
These signs may appear days or weeks before active labor.
What are the clear signs of true labor?
True labor is characterized by:
-
Regular, painful contractions that become stronger and closer together
-
Contractions that do not stop with rest
-
Progressive cervical dilation
-
Rupture of membranes (water breaking)
When should I go to the hospital at 40 weeks pregnant?
You should go to the hospital immediately if you experience:
-
Contractions every 5 minutes for at least 1 hour
-
Rupture of membranes, even without pain
-
Vaginal bleeding
-
Significant decrease in fetal movements
Is cesarean section necessary if the baby is breech at 40 weeks?
In most cases, yes. If the baby remains in a breech position at 40 weeks, cesarean delivery is generally considered the safest option. Approximately 85% of breech babies are delivered by cesarean section due to the risks of head entrapment and umbilical cord compression during vaginal breech birth.
Can a breech baby still turn at 40 weeks?
Although less common, spontaneous version can still occur late in pregnancy. Some physicians may wait briefly before scheduling a cesarean section if maternal and fetal conditions are stable.
If my first labor was difficult, will my second labor be difficult too?
Not necessarily. Each pregnancy and labor is unique. In many cases:
-
The cervix dilates faster
-
Labor is shorter
-
The body adapts more efficiently
This is especially true if the previous delivery was vaginal. If the prior birth was a cesarean without labor, outcomes may differ.
Does exercise help prepare the body for labor?
Yes. Gentle exercise can:
-
Improve circulation
-
Reduce back pain
-
Enhance physical endurance
-
Promote emotional well-being
However, exercise does not directly start labor and should remain light and medically approved.
Is induction of labor at 40 or 41 weeks safe?
When medically indicated, labor induction at 40–41 weeks is generally safe and may be safer than continuing pregnancy beyond that point. The decision depends on:
-
Cervical readiness
-
Fetal well-being
-
Maternal health conditions
What matters most when deciding between waiting, induction, or cesarean delivery?
The most important factors are:
-
Maternal safety
-
Fetal health
-
Placental function
-
Amniotic fluid levels
The goal is always a healthy mother and a healthy baby, regardless of the mode of delivery.
Final Summary of the Fortieth Week of Pregnancy
The fortieth week of pregnancy marks the completion of a full-term pregnancy and the transition toward childbirth. Labor may begin at this stage or may still be delayed — both scenarios can be completely normal.
Key points to remember:
-
The fetus is fully developed and ready for birth
-
Fetal movements should remain regular
-
Absence of labor pain is not necessarily problematic
-
Most births occur between 38 and 42 weeks
Home methods rarely induce labor reliably. Gentle activity, proper nutrition, and emotional calmness are more beneficial. If pregnancy progresses to 41 or 42 weeks, your healthcare provider will guide decisions regarding monitoring, induction, or cesarean delivery to ensure the safety of both mother and baby.
Every pregnancy and birth is unique. Trust your body, pay attention to fetal movements, avoid unnecessary comparisons, and seek medical advice when needed. Whether delivery is vaginal or by cesarean section, a successful birth is defined by the health of the mother and the newborn.





No comment